Step‑by‑step analysis of a 64‑bit Windows PE executable, focusing on entry point analysis, runtime initialization, stack frame inspection, and conditional branching to understand how user input is validated in a basic crackme challenge.
Windows PE Reverse Engineering – Crackme #2
Infos:
- Executable name: 3outof6.exe
- Format: PE32+
- Architecture: x86-64 Windows
- Sections: 19 sections
- Executable: Console
Techniques/Concepts used
- RIP-relative addressing to access data without an absolute address
- DLL imports & IAT (Import Address Table)
- Environment dependency awareness
- CRT / Runtime initialization analysis
CRT (C RunTime) all code automatically added by the compiler. RIP = address of the next instruction, used for relative addressing in x86‑64.
- Entry Point address:
0000000100401000
0000000100401000 <WinMainCRTStartup>:
100401000: 48 83 ec 28 sub rsp,0x28
100401004: 48 8d 0d 75 00 00 00 lea rcx,[rip+0x75] # 100401080 <main>
10040100b: e8 20 01 00 00 call 100401130 <cygwin_crt0>
100401010: 45 31 c0 xor r8d,r8d
100401013: 31 d2 xor edx,edx
100401015: 31 c9 xor ecx,ecx
100401017: e8 34 01 00 00 call 100401150 <cygwin_premain0>
10040101c: 45 31 c0 xor r8d,r8d
10040101f: 31 d2 xor edx,edx
100401021: 31 c9 xor ecx,ecx
100401023: e8 38 01 00 00 call 100401160 <cygwin_premain1>
100401028: 45 31 c0 xor r8d,r8d
10040102b: 31 d2 xor edx,edx
10040102d: 31 c9 xor ecx,ecx
10040102f: e8 3c 01 00 00 call 100401170 <cygwin_premain2>
100401034: 45 31 c0 xor r8d,r8d
100401037: 31 d2 xor edx,edx
100401039: 31 c9 xor ecx,ecx
10040103b: 48 83 c4 28 add rsp,0x28
10040103f: e9 3c 01 00 00 jmp 100401180 <cygwin_premain3>
We can see that the program uses cygwin, which is a large DLL that emulates Unix (POSIX) behavior on Windows.
https://cygwin.com/
Here is a simple diagram:
Program
↓
libc Cygwin
↓
cygwin1.dll
↓
Windows
The first step is to have cygwin1.dll on the system. Since the binary is dynamically linked against Cygwin, it requires this DLL to run correctly. Once the DLL is accessible (via a Cygwin installation or by placing it in the PATH or the binary folder), the standard output is visible from any Windows terminal (cmd, PowerShell, or Cygwin terminal).
All calls to Cygwin are simply initialization, so we are not interested in them.

The part that will interest us in order to better understand is the following:
sub rsp,0x28
lea rcx,[rip+0x75]
The sub rsp,0x28 is for the shadow space, a Windows convention before each call.
0x20–> shadow space0x08–> stack alignment at 16 bytes Then we load the address ofrip + 0x75, which gives us10040100b + 0x75 = 100401080.
Let’s go to the address 100401080.
0000000100401080 <main>:
100401080: 55 push rbp
100401081: 48 89 e5 mov rbp,rsp
100401084: 48 83 ec 30 sub rsp,0x30
100401088: e8 73 00 00 00 call 100401100 <__main>
10040108d: c7 45 fc 44 00 00 00 mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],0x44
100401094: 48 8d 05 65 1f 00 00 lea rax,[rip+0x1f65] # 100403000 <.rdata>
10040109b: 48 89 c1 mov rcx,rax
10040109e: e8 6d 00 00 00 call 100401110 <printf>
1004010a3: 48 8d 45 f8 lea rax,[rbp-0x8]
1004010a7: 48 89 c2 mov rdx,rax
1004010aa: 48 8d 05 66 1f 00 00 lea rax,[rip+0x1f66] # 100403017 <.rdata+0x17>
1004010b1: 48 89 c1 mov rcx,rax
1004010b4: e8 67 00 00 00 call 100401120 <scanf>
1004010b9: 8b 45 f8 mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8]
1004010bc: 39 45 fc cmp DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],eax
1004010bf: 75 11 jne 1004010d2 <main+0x52>
1004010c1: 48 8d 05 52 1f 00 00 lea rax,[rip+0x1f52] # 10040301a <.rdata+0x1a>
1004010c8: 48 89 c1 mov rcx,rax
1004010cb: e8 40 00 00 00 call 100401110 <printf>
1004010d0: eb 0f jmp 1004010e1 <main+0x61>
1004010d2: 48 8d 05 4a 1f 00 00 lea rax,[rip+0x1f4a] # 100403023 <.rdata+0x23>
1004010d9: 48 89 c1 mov rcx,rax
1004010dc: e8 2f 00 00 00 call 100401110 <printf>
1004010e1: b8 00 00 00 00 mov eax,0x0
1004010e6: 48 83 c4 30 add rsp,0x30
1004010ea: 5d pop rbp
1004010eb: c3 ret
1004010ec: 90 nop
1004010ed: 90 nop
1004010ee: 90 nop
1004010ef: 90 nop
We can see a call to <__main>, but this calls a function in cygwin1.dll, so we’re not interested in it. We can see this because if we go to address 100401100, we see a call to __imp___main, which contains __imp, so it’s a function imported from a DLL.
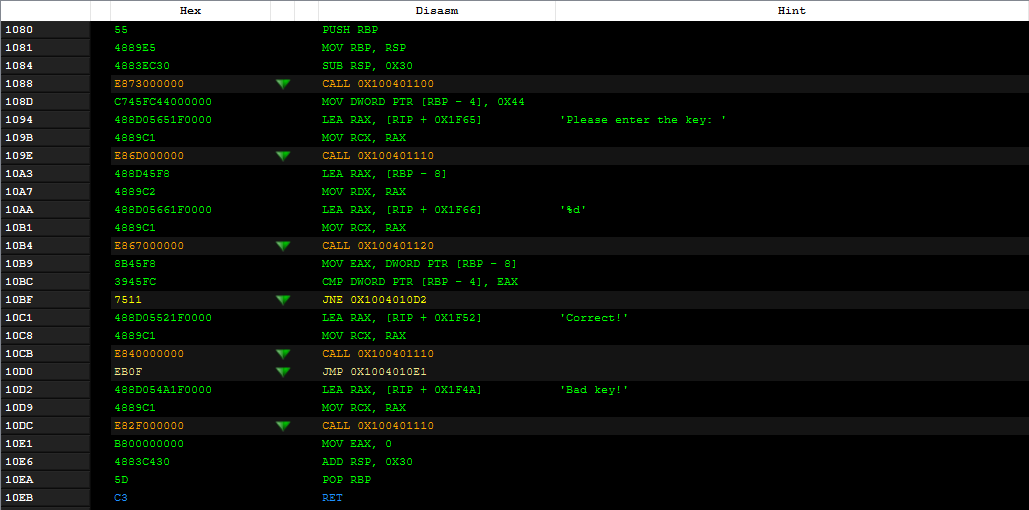
The key comparison is done with cmp DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],eax at address 1004010bc. So DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8] is the user input because before the comparison it does mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8] and then compares eax.
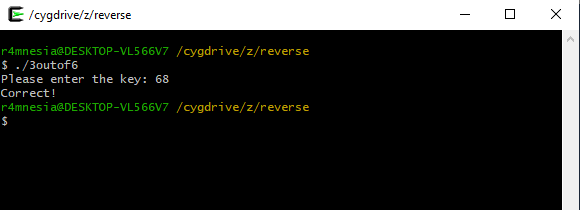
If it is not equal, it jumps to 1004010d2, which prints the message Bad key!. Thanks to the comparison, we can go back a little and see the value it puts in DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4] at address 10040108d. The value is 0x44, or 68 in decimal.